One of the main concepts in digital video and broadcasting is CDN(Content Delivery Network) structures.
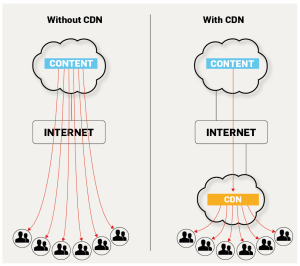
CDN infrastructure that existed before the launch of the online video market is an abstract infrastructure we can not touch.
Whether we are aware or not, we all make contact with CDNs while visiting the website during the day, watching videos, or shopping online. Firstly let’s answer the question of what is a CDN.
What we’ll cover in this post:
- What is CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
- How Does a CDN Work?
- What are CDN Types?
- What is a CDN provider?
- Which CDN Service Should be Chosen?
What is a CDN (Content Delivery Network)?
What exactly are these CDNs?
CDN stands for Content Delivery Network. The CDN structure is an economic distribution infrastructure that enables content to be delivered to the browser faster than normal.
It keeps a copy of content and videos frequently requested by a large number of Internet users, so you can get a quick response. In addition to the satisfaction of those who enter the site without delay, there is also an indirect gain.
For example, if Google sees your site open quickly, it will highlight you. In addition, the CDN structure, which reduces site load time, lowers core bandwidth consumption and reduces operational costs.
The CDN concept will be better understood when it is thought that every new person who visits the Internet is more and more impatient than the previous generation.

Today, more than half of Internet traffic is diverted by CDNs. As the number of websites targeting the global masses increases, the popularity of CDNs increases and service fees decrease. But there are also free CDN services.
How Does a CDN Work?
CDNs for video streaming are formed by connecting servers in different locations around the world. The content first reaches the nearest server from the host, then to another server, and finally to the viewer’s device.
These servers are called Internet Exchange Points. They are placed in specially designated positions to minimize delays during the stream. Thus, the latency of live streams is aimed to approach real-time.
However, distances also affect this delay. The greater the distance, the higher the number of “jumps”. For example, the closer the distance between the viewer and the broadcaster, the less distance the broadcast will travel.
What are CDN Types?
Now your question “What is a CDN?” has been answered, it is useful to look at CDN types. We can evaluate three categories according to the static and dynamic content; General content, video on demand, and live video.
Recorded video transmission is not different from a large application file. These CDNs differ from general-purpose CDNs by starting to use the media server.
When you think about the way the video is watched, you have to use the media server software because of the need for a resolution that adapts according to different speeds and because of a large number of viewers who watch the video at different points.
At the same time, this technology will also reduce the data fees that content owners have to pay. Fees are are incurred by the amount of watch time. There are not many companies that have developed media servers that allow the sending of the watched parts instead of downloading the entire video.
Recently, HTTP broadcasts often use HTTP servers (Apache or Windows Server). The HTTP broadcast is also compatible with Adaptive Bitrate (ABR). Thanks to the ABR, the videos are split into 2 to 10-second intervals to provide the viewer with optimum speed. Ant Media Server supports ABR by default.
CDN benefits in summary
- Increases content loading speed
- Blocks spams
- Allows you to control the traffic load
- Reduces bandwidth consumption
- Provides load balancing between servers
- Protect your web site against DDoS attacks.
What Are the Benefits of Using CDN for Live Streaming?
By connecting servers around the world, CDNs shorten the time required for the transmission of video streams, minimizing latency. In addition, viewers can be easily scaled thanks to CDNs.
Some advantages of streaming with CDN
Scalability. The greatest benefit CDNs offer to publishers is scalability. Scalability is very important for a successful broadcast. You don’t want to have problems reaching your audience.
Quality. The technical competence and situation of every user will not be the same. That’s why we need CDNs to deliver the best quality to every user. You will not encounter situations such as buffering with low latency provided by CDN.
Reliability. CDNs provide an extra layer of security through redundancy. Streaming through a CDN can help prevent distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks that occur when a site or resource is full by multiple concurrent breach attempts.
What is a CDN provider?
A CDN provider is a vendor that provides businesses the ability to serve their content to end-users across the world by using a content delivery network.
Which CDN Service Should be Chosen?
After asking “What is a CDN?”, “How does a CDN work?” and “What are CDN Types?” we can ask “Which one?”.
Basically, CDN vendors may shorten the loading and opening times of their content, but they may show performance differences among themselves. To see which CDN performance is better, please visit https://www.cedexis.com/get-the-data/country-report/.
All of the CDN vendors meet basic speed requirements. The difference between each vendor is milliseconds.
There are many alternatives to meet CDN needs. Vendors are generally chosen depending on POP count. As the POP count increases, the content loading speeds will increase.
For example, companies aiming to grow in Europe prefer CDN firms with a large number of POPs located in that region. In addition to the number of POPs, engineering support and urgent deletion/rescue factors should also be considered.
What’s the Live Streaming Latency in a CDN?
So now you know what is a CDN and support for HTTP based streaming is widely supported. But as demand grows with ultra-low latency streaming using WebRTC, technology is likely to shift to support WebRTC in CDNs.
Currently, its not widely support by the most popular CDN providers. If thats something essential to your business, then there are some niche CDN providers that support WebRTC, but they are few and far between.
Ant Media Server supports both scaling with CDN to play HLS, DASH(CMAF) streams and scaling real-time streaming through Ant Media Server Edge nodes. Please check the documentation if you would like to learn how to scale real-time streaming